Back pain is the most common problem faced by people. Eight in ten people will experience back pain at some point in their lifetime. Back pain affects all age groups. However, it is more commonly seen among adults aged between 35 to 45 years.
Men and women are equally affected with Low Back Pain (LBP). Even children and teens suffer from back pain.
Back pain is described as dull, shooting or piercing pain in the back. The pain aggravates with the slightest of movement, sneezing or coughing. Back pain may radiate to the abdomen, leg or foot.
How is Back Pain Caused?
Back pain is mainly caused by strained muscles or ligaments of the back, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, kidney stones, infections, fibromyalgia and endometriosis in females.
Daily activities or poor posture may also lead to back pain.
Pregnancy causes uncomfortable back pain for most of the women, but it can be managed and relieved by some simple exercises. (View Infographic on Back Pain http://www.medindia.net/health-infographics/back-pain.htm )
Smoking Linked to Back Pain
Smokers are three times more likely to suffer from back pain than non-smokers, report sources.
A recent study published in the journal Human Brain Mapping found that the connection between the two brain regions (the nucleus accumbens and the medial prefrontal cortex) plays a crucial role in chronic pain development. The research team also found that smoking affects brain circuitry linked to chronic pain by reducing the blood flow to the back and the spinal region.
Smoking reduces calcium absorption and prevents the new bone growth; this leaves the smokers with a higher risk of an osteoporotic fracture compared with non-smokers. Nicotine decreases the blood flow to the spinal region. However, it may also damage tissue in the lower back by reducing the circulation and diminishing the flow of nutrients to joints and muscles.
Hence, smokers are more prone to back pain and spine problems than non-smokers. Quitting smoking offers significant relief to people experiencing severe back pain.
Ways to Minimize the Occurrence of Back Pain
Don’t twist and bend at the same time
Lose weight to reduce the strain on the lower back.
Use ergonomics sleep mattress to keep your spine straight
Wear comfortable, low-heeled shoes
Indulge in regular exercise like walking or swimming to keep your muscle strong in your back
Avoid heavy lifting. If you do lift an object something heavy, bend your knees and keep your back straight.
Support your back while sitting, keep your back in a normal, slight arched positions
Activities such as yoga can improve the flexibility and strengthen your back muscles
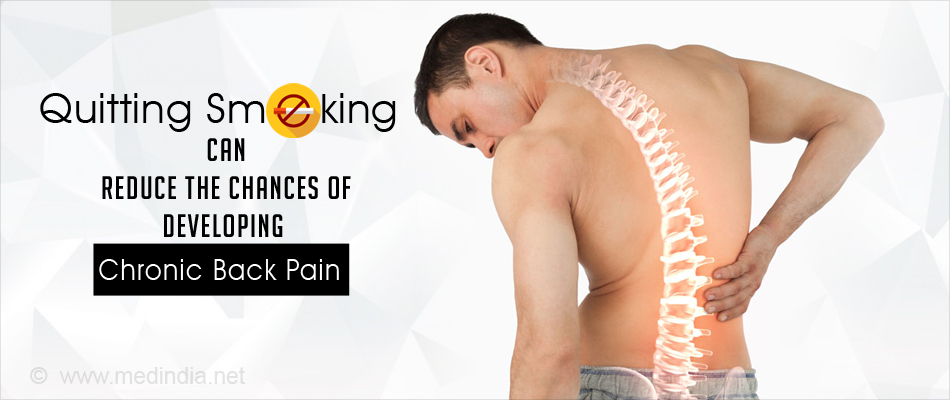
Quitting smoking can reduce the chances of developing chronic back pain
References:
http://www.quit.org.au/about/frequently-asked-questions/how-does-smoking-affect-my-body/smoking-and-back-problems.html
http://www.knowyourback.org/Pages/SpineInTheNews/FeatureArticles/BackHurtPutDownthatButt.aspx
Back pain is the most common problem faced by people. Eight in ten people will experience back pain at some point in their lifetime. Back pain affects all age groups. However, it is more commonly seen among adults aged between 35 to 45 years.
Men and women are equally affected with Low Back Pain (LBP). Even children and teens suffer from back pain.
Back pain is described as dull, shooting or piercing pain in the back. The pain aggravates with the slightest of movement, sneezing or coughing. Back pain may radiate to the abdomen, leg or foot.
How is Back Pain Caused?
Back pain is mainly caused by strained muscles or ligaments of the back, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, kidney stones, infections, fibromyalgia and endometriosis in females.
Daily activities or poor posture may also lead to back pain.
Pregnancy causes uncomfortable back pain for most of the women, but it can be managed and relieved by some simple exercises. (View Infographic on Back Pain http://www.medindia.net/health-infographics/back-pain.htm)
Smoking Linked to Back Pain
Smokers are three times more likely to suffer from back pain than non-smokers, report sources.
A recent study published in the journal Human Brain Mapping found that the connection between the two brain regions (the nucleus accumbens and the medial prefrontal cortex) plays a crucial role in chronic pain development. The research team also found that smoking affects brain circuitry linked to chronic pain by reducing the blood flow to the back and the spinal region.
Smoking reduces calcium absorption and prevents the new bone growth; this leaves the smokers with a higher risk of an osteoporotic fracture compared with non-smokers. Nicotine decreases the blood flow to the spinal region. However, it may also damage tissue in the lower back by reducing the circulation and diminishing the flow of nutrients to joints and muscles.
Hence, smokers are more prone to back pain and spine problems than non-smokers. Quitting smoking offers significant relief to people experiencing severe back pain.
Ways to Minimize the Occurrence of Back Pain
- Don’t twist and bend at the same time
- Lose weight to reduce the strain on the lower back.
- Use ergonomics sleep mattress to keep your spine straight
- Wear comfortable, low-heeled shoes
- Indulge in regular exercise like walking or swimming to keep your muscle strong in your back
- Avoid heavy lifting. If you do lift an object something heavy, bend your knees and keep your back straight.
- Support your back while sitting, keep your back in a normal, slight arched positions
- Activities such as yoga can improve the flexibility and strengthen your back muscles
- Quitting smoking can reduce the chances of developing chronic back pain
References:
http://www.quit.org.au/about/frequently-asked-questions/how-does-smoking-affect-my-body/smoking-and-back-problems.html
http://www.knowyourback.org/Pages/SpineInTheNews/FeatureArticles/BackHurtPutDownthatButt.aspx



Comments should be on the topic and should not be abusive. The editorial team reserves the right to review and moderate the comments posted on the site.